Karnaugh Map
K-map: Visual diagram that simplifies boolean algebra expressions.
Rules:
- Group adjacent 1’s in rows and columns
- Groups must contain only 1s
- Groups must be rectangles
- The sides of the rectangle must be a power of 1, 2, or 4
- Every 1 is covered by at least one group.
- There are as few groups as possible.
- Each group is as large as possible.
Examples: 2-input
AND:
OR:
XOR:
Examples: 3-input
c’:
|
a’b’ |
a’b |
ab |
ab’ |
| c’ |
1 |
1 |
1 |
1 |
| c |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
a’:
|
a’b’ |
a’b |
ab |
ab’ |
| c’ |
1 |
1 |
0 |
0 |
| c |
1 |
1 |
0 |
0 |
b:
|
a’b’ |
a’b |
ab |
ab’ |
| c’ |
0 |
1 |
1 |
0 |
| c |
0 |
1 |
1 |
0 |
bc’
|
a’b’ |
a’b |
ab |
ab’ |
| c’ |
0 |
1 |
1 |
0 |
| c |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
a’b
|
a’b’ |
a’b |
ab |
ab’ |
| c’ |
0 |
1 |
0 |
0 |
| c |
0 |
1 |
0 |
0 |
a’b + bc’:
|
a’b’ |
a’b |
ab |
ab’ |
| c’ |
0 |
1 |
1 |
0 |
| c |
0 |
1 |
0 |
0 |
3NOR: a’b’c’
|
a’b’ |
a’b |
ab |
ab’ |
| c’ |
1 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
| c |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
3XNOR:
|
a’b’ |
a’b |
ab |
ab’ |
| c’ |
1 |
0 |
1 |
0 |
| c |
0 |
1 |
0 |
1 |
- Q: How do you recognize that this is an XNOR from a’b’c’ + a’bc + abc’ + ab’c?
- A: Recognize the pattern that these are four minimizing functions that are only true when the number of 1s is odd
Majority:
|
a’b’ |
a’b |
ab |
ab’ |
| c’ |
0 |
0 |
1 |
0 |
| c |
0 |
1 |
1 |
1 |
- Q: How can we tell this a majority?
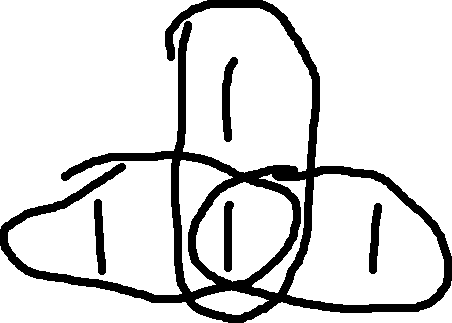
- A: We can see three groups: cb + ab + ac, which is maj(a,b,c)
Maj(a’,b,c’):
|
a’b’ |
a’b |
ab |
ab’ |
| c’ |
1 |
1 |
1 |
0 |
| c |
0 |
1 |
0 |
0 |
Maj(a’,b’,c’):
|
a’b’ |
a’b |
ab |
ab’ |
| c’ |
1 |
1 |
0 |
1 |
| c |
1 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
Examples: Four-inputs
b:
|
a’b’ |
a’b |
ab |
ab’ |
| c’d’ |
0 |
1 |
1 |
0 |
| c’d |
0 |
1 |
1 |
0 |
| cd |
0 |
1 |
1 |
0 |
| cd’ |
0 |
1 |
1 |
0 |
d:
|
a’b’ |
a’b |
ab |
ab’ |
| c’d’ |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
| c’d |
1 |
1 |
1 |
1 |
| cd |
1 |
1 |
1 |
1 |
| cd’ |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
bd:
|
a’b’ |
a’b |
ab |
ab’ |
| c’d’ |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
| c’d |
0 |
1 |
1 |
0 |
| cd |
0 |
1 |
1 |
0 |
| cd’ |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
(a+b+c+d)’:
|
a’b’ |
a’b |
ab |
ab’ |
| c’d’ |
1 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
| c’d |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
| cd |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
| cd’ |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
4XNOR:
|
a’b’ |
a’b |
ab |
ab’ |
| c’d’ |
1 |
0 |
1 |
0 |
| c’d |
0 |
1 |
0 |
1 |
| cd |
1 |
0 |
1 |
0 |
| cd’ |
0 |
1 |
0 |
1 |
???:
|
a’b’ |
a’b |
ab |
ab’ |
| c’d’ |
0 |
0 |
1 |
0 |
| c’d |
0 |
1 |
0 |
1 |
| cd |
1 |
0 |
1 |
0 |
| cd’ |
0 |
1 |
0 |
1 |
 ab+xnor(a,b,cd):
ab+xnor(a,b,cd):
|
a’b’ |
a’b |
ab |
ab’ |
| c’d’ |
1 |
0 |
1 |
0 |
| c’d |
0 |
1 |
1 |
1 |
| cd |
1 |
1 |
1 |
0 |
| cd’ |
0 |
1 |
0 |
1 |
???:
|
a’b’ |
a’b |
ab |
ab’ |
| c’d’ |
1 |
0 |
0 |
1 |
| c’d |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
| cd |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
| cd’ |
1 |
0 |
0 |
1 |
Q: What is this?
A: b’d’
Don’t Care (x)
“Don’t care”: An unknown value in a multi-valued logic system.
- As we’re trying to create groups of variables in our K-maps, we can strategically set them to create nicer groups.
Examples:
Q: What should we set X to?
A: 1
Q: What should we set X to?
|
a’b’ |
a’b |
ab |
ab’ |
| c’ |
1 |
X |
1 |
0 |
| c |
0 |
1 |
0 |
1 |
A: 0
Example: SR-Flip-Flop
This is the truth table of a SR-Flip-Flop
| S |
R |
Q^+ |
| 0 |
0 |
Q |
| 0 |
1 |
0 |
| 1 |
0 |
1 |
Now let’s construct a truth table for going from one value to another
| Q \to Q^+ |
S |
R |
| 0 \to 0 |
0 |
0 |
|
0 |
1 |
|
0 |
X |
| 0 \to 1 |
1 |
0 |
|
1 |
0 |
|
1 |
0 |
| 1 \to 0 |
0 |
1 |
|
0 |
1 |
|
0 |
1 |
| 1 \to 1 |
0 |
0 |
|
1 |
0 |
|
X |
0 |
Example: D-Flip Flop
This is the truth table of a D-Flip-Flop
Now let’s construct a truth table for going from one value to another
| Q \to Q^+ |
D |
| 0 \to 0 |
0 |
| 0 \to 1 |
1 |
| 1 \to 0 |
0 |
| 1 \to 1 |
1 |
Example: T-Flip Flop
This is the truth table of a T-Flip-Flop
Now let’s construct a truth table for going from one value to another
| Q \to Q^+ |
T |
| 0 \to 0 |
0 |
| 0 \to 1 |
1 |
| 1 \to 0 |
1 |
| 1 \to 1 |
0 |
Example: JK-Flip-Flop
This is the truth table of a JK-Flip-Flop
| J |
K |
Q^+ |
| 0 |
0 |
Q |
| 0 |
1 |
0 |
| 1 |
0 |
1 |
| 1 |
1 |
Q’ |
Now let’s construct a truth table for going from one value to another
| Q \to Q^+ |
J |
K |
| 0 \to 0 |
0 |
0 |
|
0 |
1 |
|
0 |
X |
| 0 \to 1 |
1 |
0 |
|
1 |
1 |
|
1 |
X |
| 1 \to 0 |
0 |
1 |
|
1 |
1 |
|
X |
1 |
| 1 \to 1 |
0 |
0 |
|
1 |
0 |
|
X |
0 |
As we can see, JK-flip-flop has a lot of don’t cares, which means there’s lot of choices to make in design.

 ab+xnor(a,b,cd):
ab+xnor(a,b,cd):